The subject index
/
Admiralty
hidden
|
Admiralteiskaya Embankment
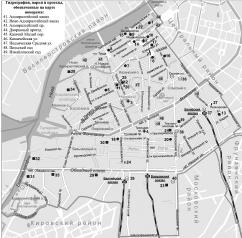
ADMIRALTEISKAYA EMBANKMENT, in 1918-44 - Roshalya Embankment in honour of revolutionary S. G. Roshal (1896-1917), lying between Dvortsovy Avenue and Dekabristov Square
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralteisky District
ADMIRALTEISKY DISTRICT, (Admiralty) an administrative territorial unit of St. Petersburg (Its territory administration is located at 10 Izmailovsky Avenue), is one of the central districts of the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralteyskaya Side
ADMIRALTEYSKAYA SIDE, a historical name of the central part of St. Petersburg bound on the north by the Neva river and on the south by the Moika River. Formed in the early 18th century when the General Admiralty
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralteysky Islands
ADMIRALTEYSKY ISLANDS, two islands, first and second, situated in the centre of St. Petersburg between the Bolshaya Nevka River and the Moika River. The first Admiralteysky Island is between Lebyazhy Canal and Winter Canal and Second Admiralteysky
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralty
ADMIRALTY, in the 18-19 centuries - a place for the building and repairing of warships, provided with all the necessary equipment (dockyards, ship-ways, slipways, storehouses, workshops, etc.). In St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralty Canal
ADMIRALTY CANAL was dug from the eastern ditch of the Amiralty Fortress (today, the Dvortsovy Bridge ramp to the Palace Square) to the Moika River to connect the Admiralty Shipyard with Galerny Dvor (Galley Yard) and warehouses of New Holland
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralty Fortress
ADMIRALTY FORTRESS, founded together with the Main Admiralty on 5 November 1704. The design of the fortress was drafted by Tsar Peter the Great under the guidance of Y.V. Bruce
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralty Shipyard
ADMIRALTY SHIPYARD, the first ship-building enterprise in St. Petersburg lay down on the left bank of the Bolshaya Neva on 5 November 1704 at the same time as the Admiralty, with chief commandant Y. V. Bruce as the construction manager
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Alexandrovsky Garden
ALEXANDROVSKY GARDEN (in 1920-89 - the Maxim Gorky Workers' Garden, in 1989-97 - Admiralty Garden) is situated along the south and the west facades of the Main Admiralty, with an area of 10 hectares. In 1805-06, gardener W
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Anniversaries of Petersburg (centenary, bicentenary, two hundred fiftieth anniversary, tercentenary)
ANNIVERSARIES OF ST. PETERSBURG. St. Petersburg's first anniversary celebration (the city's centenary) took place in 1803. Celebrations started on the morning of 16 May 1803
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Apraksin F.M., (1661-1728), Admiral
APRAKSIN Fedor Matveevich (1661-1728), Count (1709), General Admiral (1708), statesman and military officer, associate of Tsar Peter the Great. Brother of P.M. Apraksin and Tsarina Marfa, wife of Tsar Fedor Alexeevich
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bazhenov V.I., (1737-1799) architect
BAZHENOV Vasily Ivanovich (1737-1799, St. Petersburg), architect, member of the Academy of Fine Arts (1765), Member of the Russian Academy (1784), the Actual Privy Counsellor (1796). In 1756, he came to St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bolshaya Neva
BOLSHAYA NEVA, the largest left branch of the the Neva river delta; a continuation of the Neva River below the Dvortsovaya Bridge. The Bolshaya Neva flows into the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland, in the area surrounded by Vasilievsky Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bolshaya Okhta, locality
BOLSHAYA OKHTA, a locality in the east of St. Petersburg, on the right bank of the Neva River, surrounded by the Okhta River, Energetikov Avenue and Revolyutsii Freeway
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cafes (entry)
CAFES (from the French cafe, meaning coffeehouse or cafeteria). Establishments where customers were offered coffee, chocolate, pastries, and other food and beverages; most likely appeared in St. Petersburg in the early 19th century
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Canals (entry)
CANALS are artificial waterways built from the time of St. Petersburg's founding to drain low and swamp lands and create convenient access to ship construction materials and other cargoes (Peter the Great’s wish to create "a second Venice" another
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Canals of Galley Yard
CANALS OF THE GALLEY YARD were dug at the beginning of the 18th century in the western end of Admiralty Island, at the place of the Galley Yard. In 1711 and 1716
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Chevakinsky S. I. (1713-1783), architect
CHEVAKINSKY Savva Ivanovich (1713-1783), architect, representative of the Baroque. From 1729, studied at the Moscow Preparatory School of the St. Petersburg Naval Academy, in 1732-38 apprenticed in architecture with I.K
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
City Clock
CITY CLOCK. The very first mechanical clock in the city was installed in 1704 in the tower of wooden St. Peter and Paul Cathedral. In 1710, the first striker clock (with chimes) was set up on the belfry of the Church of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cruys К.I. (1657-1727), Admiral
CRUYS Kornely Ivanovich (Kornelius) (1657-1727, St. Petersburg), associate of Emperor Peter the Great, one of the founders of the Russian fleet, Admiral (1721), a Dane
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Decorative Monumental Sculpture (entry)
DECORATIVE MONUMENTAL SCULPTURE. The art of monumental sculpture dates back to the time of Peter the Great; its first examples appeared throughout St. Petersburg, at the Summer Garden and various suburb residences
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dekabristov Square
DEKABRISTOV SQUARE (prior to 1925, also called Senatskaya, Petrovskaya), is situated between Admiralteyskaya Embankment and St. Isaac Square. It appeared at the beginning of the 18th century west of the outer bank of Admiralty Fortress;
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Electrical Power Supply
ELECTRICAL POWER SUPPLY. Prototype electrical torches in St. Petersburg were lit in 1873 on Odesskaya Street. Twelve electrical torches designed by P.N. Yablochkov were installed in 1879 for the lighting of Liteiny Bridge
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Embankments (entry)
EMBANKMENTS, engineering works built along the waterways of St. Petersburg from the early 18th century in order to stabilise banks and reclaim land. The first wooden embankments appeared in Gorodskoy Island on the left bank of the Neva River between
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
February Revolution of 1917
FEBRUARY REVOLUTION OF 1917 is the Second Russian Revolution, which dethroned the Monarchy. Decisive events developed in Petrograd. On 23 February (8 March) 1917
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fire Safety
FIRE SAFETY. In the city's early days, all citizens were responsible for St. Petersburg fire safety. Soldiers of the Petersburg Garrison regularly took part in fire-extinguishing exercises
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fires (entry)
FIRES. Especially common in the first years of St. Petersburg's existence. The first large fire happened in 1710 on Troitskaya Square. A prohibition against constructing wooden houses within city limits was issued in 1727
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Founding of St. Petersburg
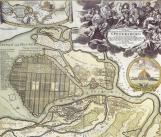
FOUNDING OF ST. PETERSBURG. In May 1703, after the surrender of Nyenschantz, Tsar Peter the Great decided to build a fortress at the mouth of the Neva River on Zayachy Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fountains (entry)
FOUNTAINS. The first fountains in St. Petersburg were laid out at the beginning of the 18th century in the Summer Garden. In 1717, the first engine was ordered (engineer Desaguliers) for their water supply and in 1717-1721 Ligovsky Canal was dug
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
General Plans for the Development of Petersburg-Leningrad
GENERAL PLANS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PETERSBURG-LENINGRAD. One the first projects of St. Petersburg planning dates back to 1709-12. According to it, the city centre should be situated at Kotlin Island and was to be connected to outer parts of the
|
|
|
|
|