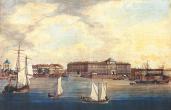The subject index
/
Senate
hidden
|
Academy of Arts
ACADEMY OF ARTS (17 Universitetskaya Embankment), state establishment of higher education in the sphere of fine arts and architecture, and a higher school of art
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Address Directories
ADDRESS DIRECTORIES, reference publications containing information about addresses of people and institutions. The first address book in St. Petersburg Address and Reference Book in Russian, German and French Languages was published in 1809 by G
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bezborodko A.A. (1747-1799), statesman
BEZBORODKO Alexander Andreevich (1747-1799, St Petersburg), Serene High Prince (1797), statesman, State Chancellor (1797). From 1765, he served at the Chancellery of the Governor-General of Malorussia (Left-Bank Ukraine)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Board of Decency
BOARD OF DECENCY, the main provincial (before 1871) and city police institution. It was created in 1782 in the course of the reform of police instead of the Main Police Office
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bobrinsky A. A. (1852-1927), public figure
BOBRINSKY Alexey Alexandrovich (1852, St. Petersburg 1927) Count, statesman and public figure, major land-owner, businessman, archaeologist, historian, senator (1896), Arch-Hoffmeister (1916). He was a son of Count Alexander A. Bobrinsky
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Chernyshevsky N. G. (1828-1889), publicist, critic, writer
CHERNYSHEVSKY Nikolay Gavrilovich (1828-1889), publicist, writer, critic. From 1846-64 lived in St. Petersburg (with an interruption from 1851-53). Graduated from the Faculty of History and Philology of Petersburg University (1850)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
City Administration (entry)
CITY ADMINISTRATION. The system of City Administration in St. Petersburg from the beginning of the 18th century developed in 2 directions - the city government and self-government (see City self-government). From 1703 the city was governed by A. D
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Civil Servants
CIVIL SERVANTS, a social-professional group forming a part of the St. Petersburg population, serving state institutions. In 1722 Emperor Peter the Great introduced a Table of Ranks
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Commission for St. Petersburg and Moscow Stone Construction
COMMISSION FOR ST. PETERSBURG AND MOSCOW STONE CONSTRUCTION was the state institution addressing the issues of urban planning and development of both capitals and other cities. It was formed on 11 December 1762 and was supervised by the Senate
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Decembrist Revolt of 1825
DECEMBRIST REVOLT OF 1825, the first overt armed revolt against autocracy and the ownership of serfs in Russia. It was prepared by the Northern Decembrist Society
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Decembrists
DECEMBRISTS, members of secret societies, mainly, Guard officers and Masonic lodge members, who excited a rebellion against autocracy and serfdom in December 1825 (hence the name). Many of the future Decembrists were born in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dekabristov Square
DEKABRISTOV SQUARE (prior to 1925, also called Senatskaya, Petrovskaya), is situated between Admiralteyskaya Embankment and St. Isaac Square. It appeared at the beginning of the 18th century west of the outer bank of Admiralty Fortress;
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
First of March 1887
FIRST OF MARCH 1887 (The Second First of March, by analogy with the First of March 1881), the day of the attempt on the life of the Emperor Alexander III. It was prepared by members of the Terrorist Faction of People's Will, created in 1886 by A.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Golovkin G.I. (1660-1734), count, statesman
GOLOVKIN Gavriil Ivanovich (1660-1734, St. Petersburg), Count of the Holy Roman Empire (1707), Count of the Russian Empire (1709), diplomat, statesman, associate of Emperor Peter the Great (half-cousin of Tsarina Natalia Kirillovna, nee Naryshkina
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Head Magistrate
HEAD MAGISTRATE, the public institution of the highest rank. It was established in St. Petersburg on the decree of tsar Peter the Great in 1720 to function as the principal establishment in charge of city magistrates of other cities and towns. In St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Highest Organs of State Power (entry)
HIGHEST ORGANS OF STATE POWER. The first higher organ of state power to function in St. Petersburg was the Senate founded by Tsar Peter the Great in 1711. The Supreme Privy Council was founded under Empress Catherine I (1725-30)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Honorary Citizen of St. Petersburg
HONORARY CITIZEN OF ST. PETERSBURG, an honorary title conferred on people who made a considerable contribution to the development of the city. In 1866-1908, 7 persons were conferred this title (the conferring didn"t entail any material privileges or
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Koni A.F. (1844-1927), lawyer, public figure
KONI Anatoly Fedorovich (1844, St Petersburg 1927, Leningrad), lawyer, statesman, man of letters, Actual Privy Counsellor (1910); Doctor of Law (1890), Honorary Member of the Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1900)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krasovsky M.V. (1851-1911), entrepreneur, public and political figure
KRASOVSKY Mikhail Vasilievich (1851-1911), public and political figure, entrepreneur, privy counsellor (1893). Graduated from the Faculty of Law of Kiev University (1871), from 1872 in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kuzmin-Karavaev V.D. (1859-1927), public figure
KUZMIN-KARAVAEV Vladimir Dmitrievich (1859-1927) was a public and political figure, lawyer, publicist, Major General (1901). On graduating from the Corps of Pages (1878) he served in Guards' Mounted-Artillery Brigade
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Laval, House of
LAVAL, HOUSE OF (4 Angliiskaya Embankment), an architectural monument of the Empire style. The first stone edifice was constructed on this place in 1719, in the middle of the 1730s it was reconstructed in the Baroque style for Count A.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Libraries (entry)
LIBRARIES. The first library of St. Petersburg was founded in 1714 by the decree of Tsar Peter the Great as His Majesty’s Library; later on, it formed the basis of the Library of the Russian Academy of Sciences
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Magistrate courts
MAGISTRATE COURTS, the lower echelon of the judiciary system introduced in the course of Judiciary reform of 1864 (see also District court). Magistrate courts were in charge of civil and minor criminal cases. The territory of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ministry of Justice
MINISTRY OF JUSTICE, one of the Russian Empire's central public institutions. Established on 8 September 1802 on the basis of the Collegium of Justice, and reached a final structure in 1811
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mirovich V. Y. (1740-1764), podporuchik
MIROVICH Vasily Yakovlevich (1740-1764, St. Petersburg), a podporuchik (sub-lieutenant) of the Smolenksky Infantry Regiment who did his military service in the garrison of Shliesselburg Fortress where ex-Emperor Ioann VI had been kept as a secret
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Orlov Family
ORLOV FAMILY, nobles, counts and princes, known since the 17th century. Brothers Grigory, Vladimir, Alexey and Fedor Orlov took an active part in the take-over of 28 June 1762
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Panin Family
PANIN FAMILY, a noble family, counts since 1767, known since the 16th century. Ivan Vasilievich Panin (1673-1736) and his cousin, Alexey Ivanovich Panin (1675-1762), Captain of the Semenovsky Life Guards Regiment
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pobedonostsev K.P. (1827-1907), statesman
POBEDONOSTSEV Konstantin Petrovich (1827-1907, St. Petersburg), statesman, lawyer, writer and translator, Full Privy Councilor (1883), Personal Secretary (1894). Graduated from the Jurisprudence College in St. Petersburg in 1846
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Political Trials of 1860-80s
POLITICAL TRIALS of 1860-80s, state trials that played the key role in the autocratic penal policy after the judicial reform of 1864. Most cases were tried in the Special Office of the Ruling Senate, doors closed and publicity confined
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Polovtsov А.А. (1832-1909) statesman, entrepreneur
POLOVTSOV Alexander Alexandrovich (1832, estate in Rapti Luzhsky Uyezd, St. Petersburg Province - 1909, same place), statesman, entrepreneur, patron of arts, Actual Privy Counsellor (1885), Secretary of State (1883)
|
|
|
|
|