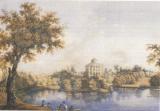Persons
/
Rossi Carl Ivanovich (Carlo Giovanni)
architect
hidden
|
Rossi C.I. (1775-1849), architect
ROSSI Carl Ivanovich (Carlo Giovanni) (1775-1849, St. Petersburg), architect. The son of the court ballerina G. Lepik. Graduated from the Peterschule in St. Petersburg, apprenticed architecture with V
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Alexandrinsky Theatre
ALEXANDRINSKY THEATRE (2 Ostrovskogo Square), called Alexandrinsky Theatre 1832-1920, it was granted the status of Academic in 1919, and in 1920 named the Petrograd (Leningrad) State Academic Drama Theatre (Akdrama, Gosdrama)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Anichkov Palace
ANICHKOV PALACE (39 Nevsky Prospect), monument of Baroque architecture. Built in 1741-54 (architect M.G. Zemtsov, G.D. Dmitriev, F. Rastrelli) near Anichkov Bridge (hence the name)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Assembly of Nobility
ASSEMBLY OF NOBILITY, St. Petersburg provincial corporate social class organisation of St. Petersburg Province nobility, founded on the basis of the Charter of Nobility dated 21 April 1785; its aim was to ensure class unity and rights of nobility
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Catherine II, Monument to
CATHERINE II, MONUMENT TO. Erected on Alexandrinskaya Square (from 1923, called Ostrovskogo Square) in front of the Alexandrinsky Theatre on 24 November 1873. The artist M.O. Mikeshin started work on the plans in 1860
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Catherine Square
CATHERINE SQUARE is situated in the centre of St. Petersburg on Nevsky Prospect. It is surrounded by the architecture ensemble of the Anichkov Palace, Alexandrinsky Theatre, and Russian National Library. The park was laid out in 1820-32 (architect K
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cavos A.K. (1800-1863), architect.
CAVOS Albert Katarinovich (1800, St. Petersburg - 1863, Peterhof), architect, representative of the late Neoclassicism of Italian descent. A son of C. A. Cavos. He studied at the University of Padua (Italy) under the guidance of C. I. Rossi
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Central Park of Culture and Recreation
CENTRAL PARK OF CULTURE AND RECREATION was opened on Elagin Island in 1931 on the basis of a park which existed from the second half of the 18th century. The park was named after S. M. Kirov from 1934 until the beginning of the 1990s
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Commandant's Department (Ordonansgaus)
COMMANDANT'S DEPARTMENT (Ordonansgaus) (3 Sadovaya Street), architectural monument of late classicism, constructed in 1824-26 (architect А.А. Mikhailov, second project of K.I. Rossi)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Committee for Construction and Water Works
COMMITTEE FOR CONSTRUCTION AND WATER WORKS was the state institution created in May 1816 on the initiative of A. A. Bethencourt for consideration of development, urban planning, and improvement projects of St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Demut-Malinovsky V.I., (1779-1846), sculptor
DEMUT-MALINOVSKY Vasily Ivanovich (1779 - 1846, St. Petersburg), sculptor. Studied at the Academy of Arts (1785-1800) under M.I. Kozlovsky, and received a retainer from the Academy of Arts to study in Rome (1803-06)
|
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
hidden
|
Elagin Palace
ELAGIN PALACE (4 Elagin Island), an Empire style architectural monument, constructed in the 1780s for I.P. Elagin, rebuilt in 1818-1822 (architect K.I. Rossi) for Empress Maria Fedorovna
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Field of Mars (Marsovo Pole), ensemble
FIELD OF MARS (in the 18th century Bolshoy Meadow, Poteshnoe Field, Tsaritsyn Meadow, in 1918 -40 – Zhertv Revolyutsii Square), the square in the centre of St. Petersburg. It was named so in honour of Mars, the Roman god of war
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fontanka, river
FONTANKA (known as Bezymyanny Erik until 1712-14), river, a branch in the Neva river delta, which crosses the central part of the city. The river flows from the Neva on the left, beside the Summer Garden
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
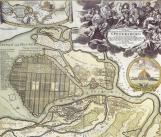
General Plans for the Development of Petersburg-Leningrad
GENERAL PLANS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PETERSBURG-LENINGRAD. One the first projects of St. Petersburg planning dates back to 1709-12. According to it, the city centre should be situated at Kotlin Island and was to be connected to outer parts of the
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
General Staff Building
GENERAL STAFF BUILDING (6-10 Dvortsovaya Embankment), architectural monument in the Empire style, in commemoration of Russia's victory in the Patriotic War of 1812 and the campaigns of 1813-14 against Emperor Napoleon I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Grilles (entry)
GRILLES. St. Petersburg boasts a number of unique metal grilles, created in the course of three centuries. Wrought grilles of bars with (sometimes gilded) decorative figures made from flat iron bars (the grille of the Ekaterininsky (Catherine)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Inzhenernaya Street
INZHENERNAYA STREET, running from Griboedova Canal to Belinskogo Square. The street was named in 1823 after the Principal Engineering College, which was located in the Mikhaylovsky Castle
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Iskusstv Square
ISKUSSTV SQUARE, situated between Inzhenernaya Street and Italyanskaya Street. Known as Mikhaylovskaya Square from 1834 to 1918, then called Lassalya Square until 1940, in memory of German socialist F. Lassal (1825-64)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Italians
ITALIANS, an ethnic community forming a part of the St. Petersburg population. The Italian language belongs to the Romance group of Indo-European languages. Believers are Catholic
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Jacot P., (1798-1860), architect.
JACOT Pavel Petrovich (1798-1860), architect and builder, representative of the late Neoclassicism. Native of France, he studied at the School of Fine Arts in Paris (1812-21) under the supervision of Debreu and L.I. Leba. In 1822 he came to St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kamenny Island, ensemble
KAMENNY ISLAND (in 1920-89 - Trudyashchikhsya Island), in the north-west part of the Neva river delta, located between the Bolshaya Nevka River to the north and the Malaya Nevka River to the south, the Krestovka River lies to the east
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Konnogvardeysky Boulevard
KONNOGVARDEYSKY BOULEVARD (in 1918-91, Profsoyuzov Boulevard), located between Dekabristov Square, St. Isaac's Square and Truda Square. The Admiralty Canal was excavated along Konnogvardeysky Boulevard in the early 18th century for transporting wood
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Landings, Water (entry)
LANDINGS, WATER. Ship landings were present in St. Petersburg from the first years of its existence. Their location depended on the location and orientation of storage warehouses
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lomonosova Square
LOMONOSOVA SQUARE (until 1948 - Chernysheva Square), between Zodchego Rossi Street and Fontanka River Embankment. It was named after M.V. Lomonosov (the first name was given after Count I.G. Chernyshev). The road was built in 1828
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Maneges (general article)
MANEGES, or riding-schools, (exerzirehaus), buildings with a large interior space, intended for troop drill exercises and cavalry dressage in fall and winter. Maneges were built in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Manezhnaya Square
MANEZHNAYA SQUARE, at the intersection of Italyanskaya Street and Karavannaya Street. It was named in 1866 after the building of Mikhailovsky Manege (1798-1800, architect V.F. Brenna; 1823-24, architect C.I. Rossi )
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Maria Fedorovna, (1759-1828), Empress
MARIA FEDOROVNA (1759-1828, St. Petersburg), Empress (from 1796). Nee Sophie Dorothea Auguste Louise, Princess of Wurttemberg. She was Emperor Pavel I's second wife (from 1776)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mikhailov, A. А. (1773-1849), architect
MIKHAILOV (Mikhailov II) Andrey Alexeevich (1773 - 1849, St. Petersburg), architect, lecturer. To discern himself from his brother, named himself Mikhailov II. Since 1779, studied at the educational school of the Petersburg Academy of Fine Arts
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mikhailovsky Castle
MIKHAILOVSKY CASTLE (since 1823, Engineer's Castle) (2 Sadovaya Street), a Neoclassical architectural monument. It was constructed in 1797-1801 (architects V.I. Bazhenov, V. F
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mikhailovsky Garden
MIKHAILOVSKY GARDEN is a landscape architectural monument from the first third of the 19th century. It is a city garden with an area of 8.7 hectares confined on one side by Mikhailovsky Palace, Griboedova Canal Embankment
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mikhailovsky Palace
Mikhailovsky Palace (2/4 Inzhenernaya Street), an architectural monument of high classicism. It was constructed from 1819-1825 for the wedding of Grand Prince Mikhail Pavlovich and Grand Princess Elena Pavlovna (architect K.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mikhaylovskaya Street
MIKHAYLOVSKAYA STREET (known as Lassalya Street from 1918 to 1940, then called Brodskogo Street until 1991), between Nevsky Prospect and Iskusstv Square. The street, laid in 1834 after the design plan conceived by architect C.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Millionnaya Street
MILLIONNAYA STREET [until 1738 - German settlement, until the middle of the 18th century - Bolshaya Nemetskaya Street, in the 1740-1800s - Bolshaya Millionnaya Street, in 1918-91 - Khalturina Street, after worker-revolutionary S.N
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ministry of Internal Affairs
MINISTRY OF INTERNAL AFFAIRS, one of the Russian Empire's central public institutions, in charge of home policy. Established on 8 September 1802, and reorganized in 1810-11
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ministry of Public Education
MINISTRY OF PUBLIC EDUCATION, central public institution, in charge of the Russian Empire's educational and academic institutions (excepting military, naval and theological institutions)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monuments to the War of 1812-1814
MONUMENTS TO THE WAR OF 1812-1814, memorial constructions in honour of Russia's military victories during the Patriotic War of 1812 and the campaigns of 1813-14 against Emperor Napoleon I concluding with allied troops marching into Paris on 19 March
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Museum of Theatre and Music Art
MUSEUM OF THEATRE AND MUSIC ART, St. Petersburg State (6 Ostrovsky Square). The museum was established in 1918 in the former apartment of the Board of Directors of Imperial Theatres, and has been at this address ever since
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Necropolis of the18th Century
NECROPOLIS OF THE 18TH CENTURY (before 1939, the Lazarevskoe Cemetery), memorial necropolis, part of the City Sculpture Museum (from 1932) on the territory of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra. Its square takes up 0.7 hectares
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Neoclassicism
NEOCLASSICISM (from the Latin сlassicus - exemplary), the style in art and architecture, based on the cult of reason and ideal order, the antique heritage being its source
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ostrovskogo Square
OSTROVSKOGO SQUARE known as Alexandrinskaya Square before 1923, between Nevsky Prospect and Zodchego Rossi Street. It was renamed after playwright A. N. Ostrovsky (1823-86). The square was designed by architect K. I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Palace Square
PALACE SQUARE, St. Petersburg's main square, the traditional location for city-wide festivities, and is part of the central square system of the Neva River's left bank
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavlovsk Museum Park
PAVLOVSK MUSEUM PARK was formed in 1918 on the palace ensemble grounds in Pavlovsk. It includes the Grand Palace, the Palace Park and the Private Garden, the Temple of Friendship, the Colonnade of Apollo, the Pil Tower, the Pavilion of Three Graces
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavlovsk, Palace and Park Ensemble
PAVLOVSK, the palace and park ensemble in the town Pavlovsk, is one of the biggest landscape parks in Europe. Its total area is 600 hectares. In 1777, the estate located here was presented by Empress Catherine II to her son Prince Pavel Pavlovich on
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavlovsk, town
PAVLOVSK, a town (from 1796), municipal unit, and the centre of the Pavlovsky District on the Slavyanka River. Known as Slutsk in 1918-44. As of 2002, the population count was approximately 16,000 inhabitants
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pimenov S.S. (1784-1833), sculptor
PIMENOV Stepan Stepanovich (1784 - 1833, St. Petersburg), sculptor. Father of N.S. Pimenov. Studied at the Academy of Arts (1795-1803) under M.I. Kozlovsky and I.P. Prokofyev
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rumyantsevsky Obelisk
RUMYANTSEVSKY OBELISK was erected by the order of Emperor Pavel I to commemorate the victories of Field Marshal General, Count P.A. Rumyantsev-Zadunaysky (see the Rumyantsevs) in the Russo-Turkish War of 1787-91
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Russian Museum, State
RUSSIAN MUSEUM, State was founded on 13 April 1895 by the decree of Emperor Nicholas II as the Russian Museum of Emperor Alexander III with the purpose of gathering the collections of Russian art
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Russian National Library
RUSSIAN NATIONAL LIBRARY (RNB) (18 Sadovaya Street), the oldest state general public library of the country, a research centre in the field of bibliology, bibliography and library science
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Russian Style
RUSSIAN STYLE. A trend in Russian architecture of the 19th - beginning of the 20th century, based on using methods and shapes of ancient and traditional Russian art and architecture. The Russian style emerged out of the aesthetics of Romanticism
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sadovaya Street
SADOVAYA STREET (from 1923 to 1944 - Third of July Street, the section from Italyanskaya Street up to Ekaterininsky Canal; from the 1730s to 1887, it was known as Bolshaya Sadovaya Street; the part from Moika River Embankment to Italyanskaya Street
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Senate
SENATE (The Ruling Senate) was the highest state institution of the Russian Empire. It was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 22 February 1711 as the highest organ of legislation, administration and judiciary
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Senate and Synod Buildings
SENATE AND SYNOD BUILDINGS (1 and 3 Decabristov Square), architectural monuments of the late Neoclassical. This ground on the embankment of the Neva River was owned by A.D. Menshikov from the early 18th century, then by A.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shuvalov (Naryshkin) Palace
SHUVALOV (NARYSHKIN) PALACE (21 Fontanka River Embankment), a 19th century architectural monument. The left part of the existing building was constructed in the 1780s in Neoclassical style (unknown architect) for Count I.I. Vorontsov
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Petrischule
ST. PETRISCHULE situated at 10 Bolshaya Konyushennaya Street, a German school attached to St. Peter's Lutheran Church, the oldest school in St. Petersburg founded c. 1710. Scientist and teacher A. F
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Stasov V.P. (1769-1848), architect
STASOV Vasily Petrovich (1769-1848, St. Petersburg), architect, representative of the Empire style. The father of V.V. Stasov. From 1783, worked in the Moscow Bureau of Architecture of the Police Department
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Summer Garden
SUMMER GARDEN (Dvortsovaya Embankment), an 18th-19th century landscaping monument. It is the oldest city garden in the central part of St. Petersburg, and is situated on the left bank of Neva, on an island formed by Fontanka River
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tauride Palace
TAURIDE PALACE (47 Shpalernaya Street), an architectural monument of Neoclassical. It was constructed in 1783-1789 (architect I.E. Starov) for Prince G.A. Potemkin-Tavrichesky (hence the name)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tyarlevo, village
TYARLEVO, formerly a village, from 1998 a municipal division in Pavlovsk administrative district located at the banks of the Tyarlevsky Brook and the Slavyanka River, and adjacent to Pavlovsky Park in the south
|
|
|
|
|